You'll dramatically improve your home's heat distribution with these seven proven insulation tricks. Start with a double-layer reflective barrier setup, maintaining proper air gaps between layers. Combine different insulation materials like fiberglass with spray foam for superior coverage. Implement strategic edge sealing using spray foam, rigid boards, or specialized tapes. Prevent thermal bridges through advanced framing techniques and continuous barriers. Design a multi-zone distribution system for targeted temperature control. Use material combinations that boost both thermal and sound performance. Create ideal ventilation flow patterns for maximum efficiency. These techniques are just the beginning of transforming your home into an energy-efficient haven.
Double-Layer Reflective Barrier Setup
When installing a double-layer reflective barrier, proper positioning and spacing are essential for maximum thermal performance.
You'll want to install the first layer perpendicular to your rafters or studs, ensuring a 2" overlap at the seams. Secure it with 1/2" self-tapping screws or staples.
For the second layer, create an air space between the layers to maximize heat reduction. You're aiming to block up to 97% of radiant heat transfer by dividing the cavity into smaller air spaces. This setup is particularly effective in metal building installations where optimal heat blocking is crucial.
Remember that each reflective surface must face an air gap to work effectively. Install thermal breaks and use furring strips if needed to maintain proper spacing.
Don't forget to keep water pipes below both layers to prevent freezing, and check for any obstructions like sprinklers or conduit before installation.
Strategic Air Gap Placement
Although air gaps might seem like empty spaces, they play an essential role in your insulation system's effectiveness.
You'll need a 50mm gap for traditional materials like fibreglass and mineral wool, while foil insulation works well with just 25mm of space.
When you're placing air gaps, make sure they're unobstructed and consistent throughout. Regular inspection helps prevent moisture problems that can severely damage your roof structure.
You'll want to integrate them with your roof's ventilation system, including ridge and soffit vents, to maintain proper airflow.
If you're using spray foam insulation, you won't need an air gap since it creates its own sealed barrier.
Edge Sealing Techniques

Effective edge sealing stands as a critical component in maximizing your insulation's performance. You'll find three primary methods to seal edges: spray foam, rigid foam boards, and specialized tapes with sealants. Each offers unique advantages for different scenarios. Proper installation requires professional guidance for optimal thermal efficiency.
| Method | Best For | R-Value/inch | Installation Ease | Durability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spray Foam | Tight spaces | R-6.5 | Moderate | Excellent |
| Rigid Foam | Open areas | R-5 | Easy | Very Good |
| Tapes/Sealants | Joints/gaps | N/A | Very Easy | Good |
| Foam Sealant | Penetrations | R-4 | Easy | Good |
| Butyl Tape | Edge joints | N/A | Very Easy | Very Good |
For ideal results, apply closed-cell spray foam in multiple ½-inch layers around rim joists and sill plates. When using rigid foam, leave a ½-inch gap for expansion and seal edges with polyurethane foam. For penetrations and joints, combine butyl flashing tape with foam sealant for complete coverage.
Thermal Bridge Prevention Methods
To prevent thermal bridges in your home's insulation system, you'll want to implement advanced framing techniques that reduce wood-to-insulation contact points and maximize insulated wall space.
You can bolster this approach by applying continuous foam sheathing to your exterior walls, creating an uninterrupted thermal barrier that wraps around studs and joints.
Ensuring gap-free installation through careful cutting, fitting, and sealing of insulation materials will maintain the integrity of your thermal envelope and prevent unwanted heat transfer. Consider installing Structural Insulated Panels during construction or renovation for superior insulation and structural performance in a single solution.
Advanced Wall Framing Techniques
When building an energy-efficient home, advanced wall framing techniques serve as your primary defense against thermal bridges.
You'll want to maximize insulation space by spacing your joists, studs, and rafters 24 inches apart on a consistent grid. This approach reduces the number of framing members while maintaining structural integrity.
Replace traditional three-stud corners with open corners or F-clips, and swap conventional partition tees for ladder-style designs.
You'll create more room for insulation while using less lumber. For headers, opt for smaller sizes and incorporate EPS or XPS foam panels instead of wood spacers.
Position your windows and doors to align with existing studs, and push headers to the exterior to create insulation voids.
Remember to implement stack framing with single top plates to guarantee direct load transfer and minimize thermal bridging throughout your walls.
Foam Sheathing Strategies
Beyond traditional framing methods, foam sheathing strategies provide a robust defense against thermal bridging in your walls.
You'll want to apply a continuous layer of rigid foam board over your wall studs to create an uninterrupted thermal barrier. This exterior insulation greatly boosts your wall's R-value and prevents heat from escaping through the framing members.
When you're installing foam sheathing, pair it with a drainable, self-adhered weather resistive barrier like HydroGap SA.
You'll need to carefully verify all water control details and changes to avoid moisture problems. If you're concerned about vapor permeability, consider using mineral wool instead of rigid foam, as it allows your wall sheathing to dry inward.
Remember to seal all seams with tape or spray foam to maintain the continuity of both thermal and air barriers.
Gap-Free Installation Methods
Since thermal bridging can greatly compromise your insulation's effectiveness, implementing gap-free installation methods requires meticulous attention to detail.
You'll need to seal all gaps, cracks, and joints before installing any insulation material. Use high-quality sealants and construction-grade tape to repair any tears in the insulation facing.
To achieve ideal results, install continuous insulation on your building's exterior, ensuring it covers all structural components uniformly.
Don't forget to incorporate thermal breaks by using low-conductivity materials between structural elements.
When installing windows and doors, position them within the insulation layer and use thermally broken frames.
Verify your work using infrared thermography to identify any remaining thermal bridges, and make necessary adjustments to create a complete thermal barrier.
Multi-Zone Heat Distribution Design
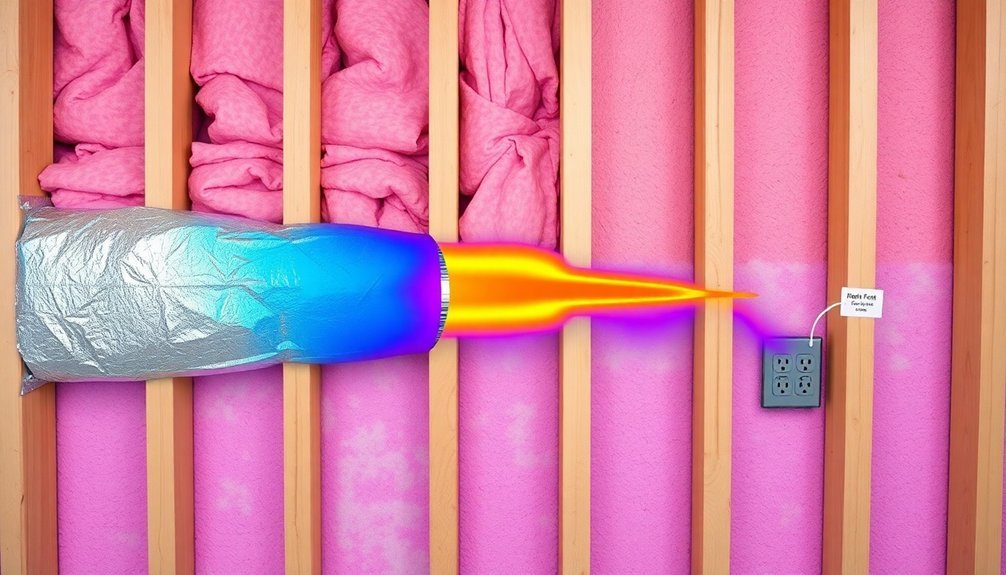

Your multi-zone heating system lets you take control of different temperature zones throughout your home, ensuring personalized comfort in each area.
You'll maximize efficiency by strategically placing dampers and thermostats to create targeted airflow patterns that match your family's daily routines and preferences.
The system's central control unit works with these components to direct heated or cooled air precisely where you need it, eliminating waste and reducing energy costs.
Zone-Based Temperature Control
Although traditional heating systems treat your entire home as one unit, zone-based temperature control offers a smarter approach by dividing your living space into distinct temperature zones.
You'll get precise control over each area through independent thermostats, whether you're managing two zones or up to seven different spaces.
This targeted approach delivers impressive benefits: you'll save energy by heating or cooling only occupied areas, reduce strain on your HVAC system, and eliminate those frustrating hot and cold spots throughout your home.
You can even integrate specialized solutions like Valor HeatSplit to distribute fireplace warmth to other rooms.
Strategic Airflow Distribution Patterns
Building on the concept of zone-based temperature control, strategic airflow distribution patterns take home comfort to the next level through sophisticated air management.
You'll want to leverage natural wind pressure and solar radiation to enhance your attic's ventilation system, ensuring air flows efficiently from soffit to ridge vents.
To maximize your system's effectiveness, you'll need to pay special attention to your insulation placement and moisture control, particularly near attic baffles and soffit regions.
Consider integrating your ventilation with your HVAC system to maintain positive indoor pressure and prevent unwanted air infiltration.
You can use the Coanda effect to your advantage by positioning supply outlets along the ceiling, which will improve air distribution throughout your rooms.
Insulation Material Combinations
Modern insulation strategies often benefit from combining different materials to maximize their effectiveness. You'll find that mixing materials like fiberglass with spray foam or mineral wool with polyurethane can greatly boost your home's thermal performance while improving sound reduction.
| Material Combo | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Fiberglass + Spray Foam | Superior gap filling, enhanced R-value |
| Mineral Wool + Polyurethane | Fire resistance, ideal heat retention |
| Cellulose + Fiberglass | Cost-effective wall filling, better density |
| Polystyrene + Mineral Wool | Excellent noise reduction, moisture control |
Ventilation Flow Pattern Control
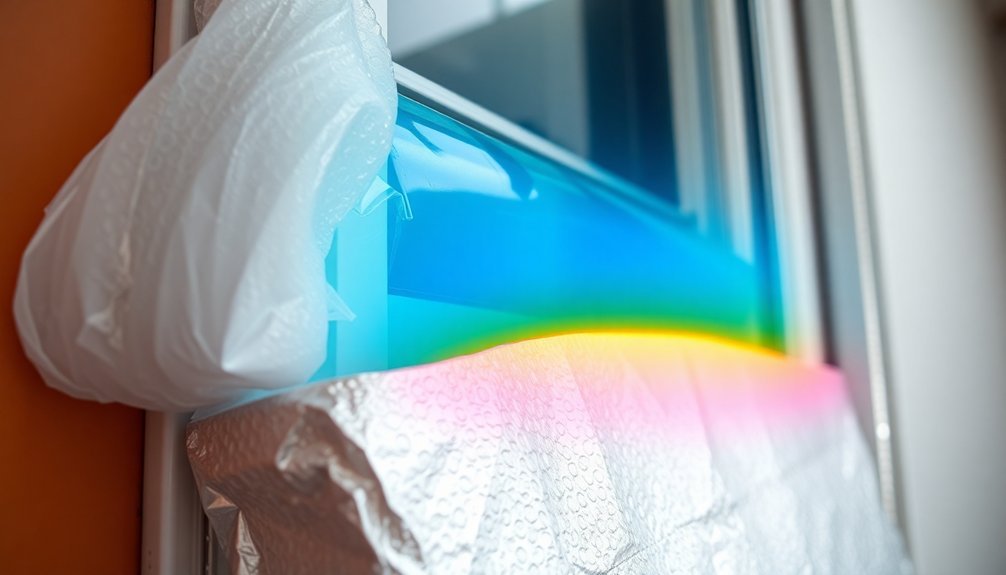

Beyond selecting the right insulation materials, proper ventilation flow patterns make a significant difference in your home's heat distribution.
You'll want to understand two main flow patterns: constant and decelerating.
Constant flow patterns, with their square or rectangular waveform, help reduce air trapping and maximize expiratory time. They're ideal when you need consistent airflow throughout your ventilation system.
In contrast, decelerating flow patterns start with high flow and gradually decrease, which can improve system synchronization and reduce pressure buildup in your ducts.
You can optimize your home's ventilation by choosing the right flow pattern for specific areas.
Use constant flow in spaces where you need steady air movement, and opt for decelerating flow in areas requiring more precise pressure control or improved air distribution efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should Insulation Be Replaced in Areas With High Humidity?
You'll need to replace fiberglass insulation every 15-20 years, cellulose every 10-15 years, and spray foam every 60-70 years in high humidity. Regular inspections help you catch moisture damage early.
Can Mixing Different Types of Insulation Materials Affect Their Individual Performance?
Yes, when you mix insulation types correctly, they'll complement each other's strengths. However, if you combine them improperly, you could reduce their effectiveness and create gaps in thermal or moisture protection.
What Temperature Differences Indicate Poor Insulation Distribution in Specific Rooms?
If you notice temperature differences of more than 5-10 degrees between rooms, it's a sign of poor insulation. You'll especially feel this in rooms above uninsulated spaces or those with exterior walls.
Do Smart Thermostats Actually Improve Insulation Efficiency in Multi-Story Homes?
Yes, your smart thermostat can improve insulation efficiency by detecting temperature variations between floors and adjusting airflow accordingly. It'll learn your home's heating patterns and optimize HVAC performance for better temperature distribution.
Should Insulation Installation Timing Vary Based on Seasonal Temperature Changes?
Yes, you'll want to schedule insulation during mild seasons like spring or fall. This timing helps guarantee proper installation conditions and lets you prepare your home before extreme temperatures hit, maximizing energy efficiency.
In Summary
You'll maximize your home's heat efficiency by implementing these seven proven insulation strategies. Start with the double-layer reflective barriers and strategic air gaps, then focus on sealing edges and preventing thermal bridges. Don't forget to combine different insulation materials and control your ventilation patterns. These techniques work together to create an ideal thermal envelope that'll keep your space comfortable while reducing energy costs.




Leave a Reply